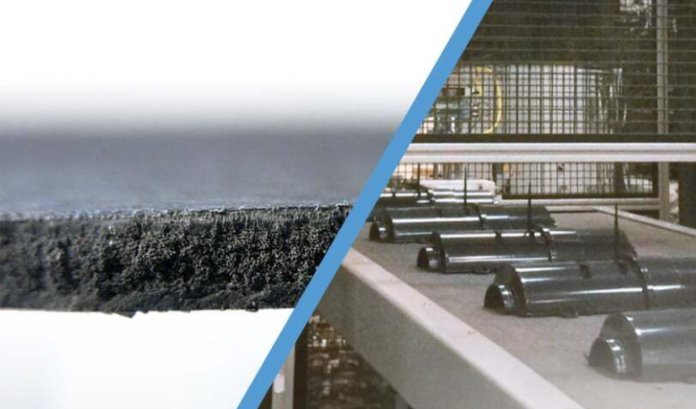
Structural foam molding is a versatile manufacturing process that offers numerous advantages for producing large, complex plastic parts with exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. Structural foam molding is widely used across various industries, from automotive components to furniture pieces, to create durable, lightweight, and cost-effective products. This comprehensive article explores the advantages of structural foam molding, its applications, and why it’s a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking high-quality, efficient production solutions.
Understanding Structural Foam Molding
Structural foam molding is an injection molding process that utilizes a chemical blowing agent to create a cellular structure within the plastic part. Unlike traditional injection molding, which uses a high-pressure injection to fill the mold cavity, structural foam molding injects a foaming agent into the melted plastic resin, causing it to expand and fill the mold with a cellular structure. This results in lighter, more robust, and more rigid than solid plastic parts. Explore online, where you can learn more about structural foam and gain insights into its advantages, applications, and best practices for implementation. Manufacturers can optimize their production processes and leverage the benefits of this innovative manufacturing technology by researching structural foam molding techniques and staying informed about industry developments.
Advantages of Structural Foam Molding
1. Lightweight Design: A primary advantage of structural foam molding is that it can produce lightweight parts without sacrificing strength or structural integrity. The cellular structure created during the molding process reduces the overall density of the part, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as automotive components, consumer goods, and industrial equipment.
2. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Despite their lightweight design, parts produced using structural foam molding exhibit exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. The cellular structure provides added rigidity and strength, making structural foam-molded parts suitable for load-bearing applications and environments where durability and impact resistance are essential.
3. Cost-Effective Production: Structural foam molding offers cost-effective production solutions for manufacturing large, complex plastic parts. The process requires less material than solid injection molding, reducing material costs. Structural foam molding can also produce thick-walled parts with uniform wall thicknesses, eliminating the need for costly secondary operations.
4. Fast Cycle Times: Structural foam molding typically has shorter cycle times than other molding processes, allowing for high-volume production of parts with fast turnaround times. The foaming agent facilitates rapid filling of the mold cavity, resulting in shorter cooling times and increased productivity. This makes structural foam molding an efficient and economical choice for manufacturers looking to meet tight production schedules and customer demands.
5. Design Flexibility: Structural foam molding offers design flexibility, allowing for the production of complex geometries, intricate details, and undercuts that may be difficult or impossible to achieve with other molding processes. The ability to mold large, thick-walled parts with uniform wall thicknesses opens up a wide range of design possibilities, enabling manufacturers to create innovative products meeting the specific requirements of their applications.
6. Noise and Vibration Dampening: The cellular structure of parts produced using structural foam molding provides inherent noise and vibration dampening properties, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction and vibration absorption are essential considerations. Structural foam-molded parts are commonly used in automotive interiors, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics to enhance user comfort and reduce noise levels.
7. Chemical and Corrosion Resistance: Structural foam-molded parts exhibit excellent chemical and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments and demanding applications where exposure to chemicals, solvents, and corrosive substances is every day. The closed-cell structure of the foam offers a barrier against moisture and chemical ingress, ensuring long-term durability and performance of the parts.
8. Environmental Sustainability: Structural foam molding is a sustainable manufacturing process that minimizes waste and energy consumption. Using less material reduces the amount of waste generated during production, while shorter cycle times and lower energy requirements contribute to overall energy efficiency. Additionally, structural foam-molded parts are fully recyclable at the end of their service life, reducing their environmental impact.
Applications of Structural Foam Molding
Structural foam molding is used across various industries and applications due to its numerous advantages and versatility. Some common applications of structural foam-molded parts include:
* Automotive components include bumpers, dashboards, instrument panels, and interior trim.
* Industrial equipment and machinery components require high strength, durability, and impact resistance.
* Furniture pieces such as chairs, tables, and storage cabinets require lightweight design and structural integrity.
* Material handling and storage containers for transporting goods and materials in industrial and commercial settings.
* Consumer goods such as recreational equipment, sporting goods, and outdoor furniture require lightweight, durable construction.
Structural foam molding offers numerous advantages for manufacturers seeking efficient, cost-effective solutions for producing large, complex plastic parts with exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. Structural foam-molded parts are used across various industries and applications, from lightweight automotive components to durable industrial equipment, due to their high strength, lightweight design, cost-effectiveness, and design flexibility. By understanding the advantages of structural foam molding and its applications, manufacturers can leverage this versatile manufacturing process to create innovative products that meet the demands of today’s market while maximizing efficiency and productivity.