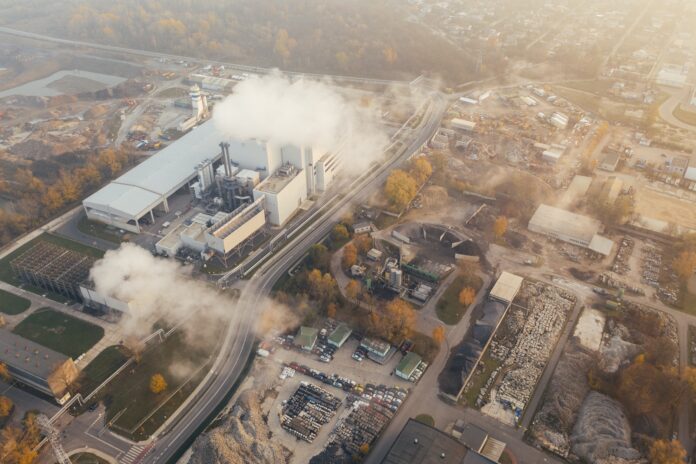
Decarbonization has emerged as a crucial and pressing global initiative in response to the escalating threat of climate change. This process aims to reduce or eliminate carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from various sectors, such as energy, transportation, industry, and agriculture, to mitigate the impacts of greenhouse gases on the Earth’s climate system. As the world grapples with the urgent need to address climate change, decarbonization has gained significant attention from policymakers, scientists, businesses, and society at large.
Decarbonization is a multifaceted concept encompassing a wide range of strategies, technologies, and policies that can contribute to the reduction of carbon emissions. At its core, decarbonization involves transitioning from fossil fuel-based energy sources, which are the primary culprits behind CO2 emissions, to low-carbon or carbon-free alternatives. This transition requires significant shifts in energy production and consumption patterns, as well as changes in industrial processes and land use practices.
One of the key drivers behind decarbonization is the recognition of the detrimental effects of greenhouse gas emissions on the global climate system. The accumulation of CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere traps heat, leading to a rise in global temperatures, altered weather patterns, and intensified natural disasters. These impacts pose severe risks to ecosystems, human health, and socio-economic stability. Decarbonization, therefore, serves as a critical pathway to mitigate these risks and build a more sustainable future.
The urgency of decarbonization is underscored by the increasing frequency and intensity of climate-related events, such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and heatwaves. These events not only endanger lives and livelihoods but also impose substantial economic costs on communities and nations. By reducing carbon emissions, decarbonization aims to limit the magnitude and severity of climate-related events, enhancing resilience and adaptive capacity to withstand future challenges.
Decarbonization encompasses a broad spectrum of strategies and approaches that can be tailored to different sectors and regions based on their unique circumstances and available resources. One of the primary areas of focus is the energy sector, which accounts for a significant portion of global carbon emissions. The transition from fossil fuel-based energy to renewable sources, such as solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal, lies at the heart of decarbonization efforts. The adoption of renewable energy technologies, coupled with improvements in energy efficiency, can lead to substantial emissions reductions while simultaneously promoting energy security and independence.
In addition to the energy sector, transportation represents another critical domain for decarbonization. The reliance on fossil fuel-powered vehicles, particularly those running on gasoline and diesel, contributes significantly to CO2 emissions. Decarbonizing the transportation sector involves transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs), improving public transportation systems, promoting cycling and walking, and investing in infrastructure for alternative fuels like hydrogen. Such measures can not only reduce carbon emissions but also alleviate air pollution and enhance urban livability.
Furthermore, decarbonization extends to industrial processes and manufacturing, which are responsible for a substantial share of global emissions. Industrial decarbonization involves deploying cleaner technologies, improving energy efficiency, and exploring carbon capture and storage (CCS) solutions. The adoption of circular economy principles, which emphasize the recycling and reuse of materials, can also contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of industries.
Agriculture and land use practices represent yet another dimension of decarbonization. These sectors are responsible for emissions of greenhouse gases such as methane and nitrous oxide, primarily through livestock production, rice cultivation, and deforestation. Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, such as precision farming, agroforestry, and regenerative techniques, can help sequester carbon in soils and reduce emissions from the agricultural sector.
Decarbonization requires not only technological advancements but also robust policy frameworks and institutional support. Governments play a crucial role in setting ambitious emissions reduction targets, enacting regulations and incentives, and fostering international collaborations to drive decarbonization efforts. Policy mechanisms such as carbon pricing, subsidies for renewable energy, and research and development funding can incentivize the adoption of low-carbon technologies and spur innovation in decarbonization pathways.
Furthermore, private sector engagement is vital for decarbonization to thrive. Businesses can contribute to decarbonization by incorporating sustainability principles into their operations, investing in clean technologies, and setting science-based emission reduction targets. Collaboration between governments, businesses, and civil society organizations is also essential for sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices to accelerate the decarbonization transition.
The benefits of decarbonization extend beyond environmental gains. The shift to a low-carbon economy can stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and enhance energy security. The renewable energy sector, in particular, has the potential to generate employment opportunities and attract investments. By fostering innovation and embracing the green economy, countries can position themselves at the forefront of the transition and reap the economic rewards of decarbonization.
However, decarbonization is not without its challenges. The scale and complexity of the transition require significant investments in infrastructure, research and development, and capacity building. The costs associated with decarbonization can pose short-term challenges for some industries and economies. Moreover, the transition must be managed in a just and equitable manner, ensuring that vulnerable communities and workers are not left behind. Social inclusiveness, along with the consideration of environmental justice, should be integral to the decarbonization agenda.
Decarbonization represents a transformative pathway to address the urgent issue of climate change. By reducing carbon emissions across sectors, transitioning to low-carbon technologies, and implementing supportive policies, decarbonization offers a viable solution to mitigate the impacts of climate change. It is a multifaceted endeavor that requires collaborative efforts from governments, businesses, and individuals to drive the necessary transformations. Through decarbonization, we can pave the way towards a sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.
Furthermore, decarbonization necessitates a comprehensive approach that integrates various strategies and initiatives. One key aspect is the deployment of advanced renewable energy technologies. Solar power, for instance, has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years, with increasing efficiency and declining costs of photovoltaic panels. Similarly, wind power has emerged as a significant contributor to the global energy mix, thanks to technological innovations and large-scale wind farms. Other renewable sources like hydropower, geothermal energy, and tidal power also hold immense potential for decarbonization.
To facilitate the integration of renewable energy into existing grids, energy storage technologies play a crucial role. Batteries, such as lithium-ion and flow batteries, are becoming more efficient and affordable, enabling the storage of surplus renewable energy for use during periods of low generation. Moreover, emerging technologies like hydrogen fuel cells and power-to-gas systems offer promising solutions for long-term energy storage and the decarbonization of sectors such as transportation and industry.
Energy efficiency measures are equally important in the decarbonization agenda. By reducing energy consumption through efficient building design, smart grids, and energy-efficient appliances, significant carbon savings can be achieved. Energy management systems, including demand response mechanisms and real-time energy monitoring, can optimize energy usage and reduce waste. Additionally, retrofitting existing buildings to enhance their energy efficiency and promoting sustainable urban planning can contribute to substantial emissions reductions.
Decarbonization also entails a shift in the mindset and behavior of individuals and communities. Adopting sustainable lifestyles, such as embracing public transportation, reducing waste, and opting for plant-based diets, can significantly lower carbon footprints. Education and awareness campaigns are essential for fostering behavioral change and promoting sustainable consumption patterns. Governments and organizations can play a pivotal role in encouraging sustainable practices through incentives, public campaigns, and the provision of infrastructure that supports greener choices.
International cooperation and collaboration are crucial for achieving effective decarbonization on a global scale. The Paris Agreement, signed by almost all nations, sets the framework for collective action to combat climate change and pursue decarbonization goals. The agreement emphasizes the need for countries to regularly report their emissions and progress towards their targets, fostering transparency and accountability. Additionally, international initiatives and platforms facilitate the sharing of best practices, technology transfer, and financial support to enable developing nations to pursue sustainable development pathways.
In conclusion, decarbonization is a multifaceted and complex process that requires concerted efforts from all stakeholders. It necessitates the widespread deployment of renewable energy technologies, the promotion of energy efficiency measures, and the adoption of sustainable practices at individual and societal levels. Governments, businesses, and individuals must collaborate to create enabling policy frameworks, invest in research and development, and foster innovation in low-carbon solutions. The benefits of decarbonization extend beyond mitigating climate change and include economic growth, job creation, improved energy security, and enhanced quality of life. By embracing decarbonization as a collective global endeavor, we can pave the way for a sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.