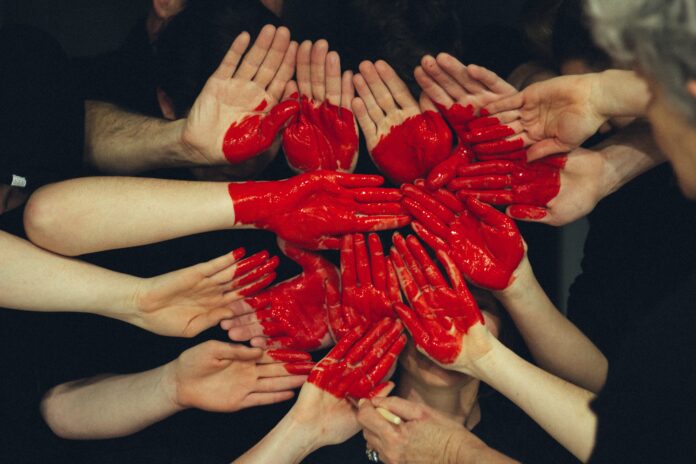
Xenophobia is a complex and deeply rooted phenomenon that refers to the fear, hatred, or prejudice against individuals or groups who are perceived as foreign or different from one’s own cultural, ethnic, or national identity. The term “xenophobia” is derived from the Greek words “xenos” meaning “stranger” or “foreigner” and “phobos” meaning “fear.” It manifests in various forms, ranging from subtle biases and stereotypes to overt acts of discrimination, hostility, or violence towards individuals or communities.
Understanding xenophobia requires delving into its historical, social, and psychological dimensions. Throughout history, human societies have often exhibited a tendency to view those who are different with suspicion, distrust, or hostility. Xenophobia can emerge as a response to cultural, economic, political, or demographic changes, and it can be fueled by ignorance, misinformation, or a desire to protect one’s own perceived interests.
Xenophobia can target various aspects of identity, such as race, ethnicity, nationality, religion, language, or immigration status. It can be directed towards individuals or groups who are perceived as outsiders, immigrants, refugees, or people seeking asylum. Xenophobic attitudes and behaviors can be observed at the individual, societal, and systemic levels, permeating interpersonal interactions, public discourse, and institutional policies.
Now, let’s explore ten important aspects related to xenophobia:
1. Historical Roots: Xenophobia has existed for centuries and has been a recurring feature of human societies. From ancient civilizations to contemporary times, examples of xenophobia can be found in various forms, often tied to specific historical, political, or social contexts.
2. Global Phenomenon: Xenophobia is not limited to any specific region or culture. It can be observed in different parts of the world, albeit with varying degrees of intensity and manifestations. Xenophobia can be present in developed and developing countries alike.
3. Causes and Triggers: Xenophobia can be triggered by a range of factors, such as economic instability, social change, political turmoil, and cultural clashes. Economic downturns, scarcity of resources, and perceived threats to national identity or security are often associated with increased xenophobic sentiments.
4. Stereotypes and Prejudices: Xenophobia often relies on stereotypes and prejudices to dehumanize and vilify the targeted group. These stereotypes can be perpetuated through media, cultural narratives, or social norms, contributing to the reinforcement of xenophobic attitudes.
5. Impact on Individuals and Communities: Xenophobia has significant psychological, social, and economic consequences for both individuals and communities. It can lead to discrimination, social exclusion, marginalization, reduced access to resources and opportunities, and a negative impact on mental health and well-being.
6. Intersectionality: Xenophobia intersects with other forms of discrimination, such as racism, sexism, or religious intolerance. Individuals who belong to multiple marginalized groups may experience compounded forms of discrimination and face unique challenges.
7. Rise of Nationalism and Populism: Xenophobia can be intertwined with nationalist and populist movements that seek to promote the interests of a particular group or nation. These ideologies often scapegoat immigrants or minority groups, exacerbating xenophobic sentiments.
8. Role of Media and Technology: Media and technology play a crucial role in shaping public perceptions and attitudes towards different groups. Biased reporting, misinformation, or the spread of xenophobic narratives through social media platforms can contribute to the normalization of xenophobic ideas.
9. Human Rights and Legal Frameworks: Xenophobia raises important human rights concerns. International human rights instruments and domestic legal frameworks aim to address and prevent xenophobia, promoting equality, non-discrimination, and protection of the rights of all individuals, regardless of their background.
10. Countering Xenophobia: Combating xenophobia requires a multifaceted approach that involves education, awareness-raising, policy interventions, and fostering inclusive societies. Here are some strategies and initiatives aimed at countering xenophobia:
Education and Awareness: Promoting education that emphasizes diversity, multiculturalism, and the appreciation of different cultures can help challenge xenophobic attitudes and stereotypes. Creating opportunities for intercultural exchanges, dialogue, and understanding can also contribute to reducing xenophobia.
Community Engagement: Encouraging community engagement and fostering intergroup interactions can help break down barriers and promote empathy. Building bridges between different communities through cultural events, community projects, and grassroots initiatives can foster a sense of belonging and unity.
Promoting Inclusive Policies: Implementing inclusive policies that protect the rights of immigrants, refugees, and minority groups is crucial in combating xenophobia. This includes fair immigration laws, anti-discrimination measures, and policies that promote equal access to education, employment, and healthcare.
Media Literacy: Enhancing media literacy skills among individuals can empower them to critically analyze media content, identify biases, and challenge xenophobic narratives. Media organizations should also be encouraged to promote responsible reporting and avoid sensationalism or stigmatization.
Intercultural Dialogue: Facilitating platforms for intercultural dialogue, such as community forums, workshops, or online discussions, can encourage open and respectful conversations between diverse groups. These dialogues can help address misunderstandings, challenge stereotypes, and promote mutual understanding.
Legal Protection and Enforcement: Strengthening legal frameworks that protect individuals from xenophobic acts and ensuring their effective enforcement is essential. Punishing hate crimes, discrimination, and xenophobic speech can send a strong message that such behavior will not be tolerated.
International Cooperation: Addressing xenophobia requires international cooperation and collaboration. Sharing best practices, exchanging experiences, and working together to address the root causes of xenophobia can contribute to global efforts in combating this issue.
Advocacy and Empowerment: Supporting grassroots organizations, NGOs, and civil society groups that actively work to counter xenophobia is crucial. These organizations play a vital role in advocating for the rights of marginalized communities, raising awareness, and providing support to victims of xenophobia.
Political Leadership and Public Discourse: Political leaders have a responsibility to promote inclusive and tolerant societies. They should condemn xenophobic rhetoric, promote diversity, and actively engage in constructive public discourse that emphasizes the value of multiculturalism and inclusivity.
Social Integration: Encouraging social integration between immigrant communities and the host society can help foster a sense of belonging and reduce xenophobia. This includes providing language and cultural orientation programs, promoting employment opportunities, and facilitating social interactions.
It is important to note that combating xenophobia is an ongoing and complex process that requires long-term commitment, collaboration, and a comprehensive approach involving multiple stakeholders. By addressing the underlying causes, promoting understanding, and ensuring the protection of human rights, societies can strive towards inclusivity, acceptance, and a rejection of xenophobia.
Let’s delve deeper into xenophobia, exploring its manifestations, impacts, and potential solutions in more detail.
Xenophobia is a multifaceted phenomenon that manifests in various ways, ranging from subtle biases and prejudices to overt acts of discrimination, hostility, or violence. It can be directed towards individuals or groups who are perceived as outsiders, immigrants, refugees, or people seeking asylum. Xenophobic attitudes and behaviors can be observed at the individual, societal, and systemic levels, permeating interpersonal interactions, public discourse, and institutional policies.
One of the key aspects of xenophobia is the tendency to view those who are different as a threat. This threat perception can arise from various factors, including economic competition, cultural clashes, fear of change, and concerns about national identity or security. Economic downturns, job scarcity, or perceptions of resource strain can amplify xenophobic sentiments, as people may blame immigrants or minority groups for their economic struggles.
Xenophobia often relies on stereotypes and prejudices to dehumanize and vilify the targeted group. These stereotypes can be perpetuated through media, cultural narratives, or social norms, contributing to the reinforcement of xenophobic attitudes. For example, immigrants may be portrayed as criminals, job stealers, or cultural invaders, reinforcing negative perceptions and fostering fear or resentment.
The impact of xenophobia is far-reaching, affecting both individuals and communities. Individuals who are targets of xenophobia can face discrimination, social exclusion, and marginalization. They may experience limited access to resources, opportunities, and basic services like healthcare or education. The psychological toll of xenophobia can be significant, leading to increased stress, anxiety, depression, and a sense of alienation.
Xenophobia also has broader societal implications. It erodes social cohesion, hampers community integration, and undermines the principles of equality, diversity, and human rights. It perpetuates divisions within society, hindering cooperation, empathy, and mutual understanding. By fostering an environment of fear and distrust, xenophobia obstructs the building of inclusive and harmonious societies.
Furthermore, xenophobia intersects with other forms of discrimination, such as racism, sexism, or religious intolerance. Individuals who belong to multiple marginalized groups may experience compounded forms of discrimination and face unique challenges. This intersectionality underscores the need for an inclusive approach that recognizes and addresses the overlapping dimensions of discrimination and prejudice.
Understanding the causes and drivers of xenophobia is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat it. Economic factors, such as unemployment or inequality, can create fertile ground for xenophobic sentiments to take hold. Political factors, including the rise of nationalist or populist movements, can exploit xenophobia for their own agendas. Social and cultural factors, such as the perpetuation of stereotypes or the lack of intercultural dialogue, can also contribute to the persistence of xenophobia.
Addressing xenophobia requires a multifaceted and comprehensive approach involving various stakeholders and strategies. Here are some key areas of focus:
Education and Awareness: Promoting education that emphasizes diversity, multiculturalism, and the appreciation of different cultures is essential in countering xenophobia. Schools, colleges, and educational institutions can incorporate curricula that promote empathy, critical thinking, and intercultural understanding. Education should also include accurate historical narratives, debunking stereotypes and biases.
Community Engagement: Encouraging community engagement and fostering intergroup interactions can help break down barriers and promote empathy. Building bridges between different communities through cultural events, community projects, and grassroots initiatives can foster a sense of belonging and unity. Local organizations and community leaders play a crucial role in facilitating such interactions.
Promoting Inclusive Policies: Implementing inclusive policies that protect the rights of immigrants, refugees, and minority groups is crucial in combating xenophobia. This includes fair immigration laws, anti-discrimination measures, and policies that promote equal access.
Promoting Inclusive Policies: Implementing inclusive policies that protect the rights of immigrants, refugees, and minority groups is crucial in combating xenophobia. This includes fair immigration laws, anti-discrimination measures, and policies that promote equal access to education, employment, healthcare, and housing. Governments should strive to create an environment that celebrates diversity and ensures the full participation and integration of all individuals, regardless of their background.
Media Literacy: Enhancing media literacy skills among individuals is essential in countering xenophobia. People should be equipped with the ability to critically analyze media content, identify biases, and challenge xenophobic narratives. Media organizations should also be encouraged to promote responsible reporting, avoiding sensationalism, stigmatization, or the perpetuation of stereotypes. Efforts should be made to foster a media landscape that values accuracy, diversity, and unbiased representation.
Intercultural Dialogue: Facilitating platforms for intercultural dialogue, such as community forums, workshops, or online discussions, can encourage open and respectful conversations between diverse groups. These dialogues can help address misunderstandings, challenge stereotypes, and promote mutual understanding. Encouraging individuals from different backgrounds to engage in meaningful interactions fosters empathy,
Legal Protection and Enforcement: Strengthening legal frameworks that protect individuals from xenophobic acts and ensuring their effective enforcement is essential. Hate crime laws should be in place to provide legal recourse for victims. Law enforcement agencies should receive proper training on identifying and addressing xenophobic incidents. Additionally, mechanisms for reporting and documenting xenophobic incidents should be established to track and address the prevalence of such acts.
International Cooperation: Addressing xenophobia requires international cooperation and collaboration. Countries should work together to share best practices, exchange experiences, and develop joint initiatives to combat xenophobia. This includes sharing knowledge on successful integration models, supporting each other in resettlement efforts, and fostering dialogue on global migration challenges. International organizations, such as the United Nations and regional bodies, can play a vital role in coordinating these efforts.
Advocacy and Empowerment: Supporting grassroots organizations, NGOs, and civil society groups that actively work to counter xenophobia is crucial. These organizations play a vital role in advocating for the rights of marginalized communities, raising awareness, providing support to victims of xenophobia, and engaging in dialogue with policymakers. Empowering affected communities by providing them with a platform to voice their concerns and participate in decision-making processes is essential in challenging xenophobic attitudes.
Political Leadership and Public Discourse: Political leaders have a responsibility to promote inclusive and tolerant societies. They should publicly condemn xenophobic rhetoric, promote diversity, and actively engage in constructive public discourse that emphasizes the value of multiculturalism and inclusivity. Political campaigns and public speeches should focus on unity, respect, and equal rights for all, sending a clear message that xenophobia will not be tolerated.
Social Integration: Encouraging social integration between immigrant communities and the host society can help foster a sense of belonging and reduce xenophobia. This includes providing language and cultural orientation programs for newcomers, promoting employment opportunities and economic empowerment, and facilitating social interactions through community centers, sports clubs, or cultural events. Building inclusive neighborhoods and fostering a sense of shared identity can help mitigate xenophobic attitudes and promote social cohesion.
It is important to recognize that combating xenophobia is a continuous process that requires long-term commitment and collaboration. Efforts to address xenophobia should go beyond reactive measures and focus on addressing the underlying causes, including socio-economic disparities, cultural misunderstandings, and systemic discrimination. By fostering an environment of inclusivity, empathy, and respect for diversity, societies can strive towards a future free from xenophobia.