Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. It is a significant environmental issue that has garnered widespread attention in recent decades. The consequences of global warming are far-reaching, impacting various aspects of life on Earth, including ecosystems, weather patterns, sea levels, and human societies. In this comprehensive exploration of global warming, we will delve into its causes, effects, and potential solutions, aiming to provide a holistic understanding of this pressing global concern.
The primary driver of global warming is the excessive release of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun, causing a greenhouse effect that warms the planet’s surface. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels for energy production, industrial processes, deforestation, and agriculture, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This enhanced greenhouse effect leads to a gradual rise in global temperatures, known as global warming.
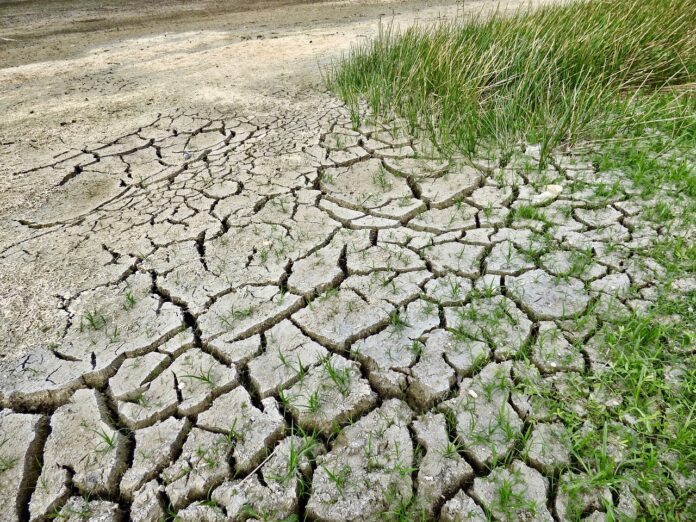
The consequences of global warming are vast and impactful. Rising temperatures have far-reaching effects on the Earth’s ecosystems, including shifts in wildlife habitats, changes in species distribution and migration patterns, and increased extinction risks. Ecosystems that rely on specific temperature ranges, such as coral reefs and polar regions, are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of global warming. As temperatures rise, coral bleaching occurs, leading to the death of reefs and the loss of valuable marine biodiversity. In polar regions, the melting of ice caps and glaciers threatens the survival of species like polar bears and penguins, while also contributing to rising sea levels.
Another significant consequence of global warming is the alteration of weather patterns and the increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. As the Earth’s atmosphere heats up, it disrupts atmospheric circulation patterns, leading to changes in rainfall patterns, droughts, heatwaves, and more severe storms. These events pose risks to human lives, infrastructure, agriculture, and freshwater resources. Additionally, global warming contributes to the intensification of tropical cyclones, such as hurricanes and typhoons, resulting in devastating impacts along coastal areas.
One of the most concerning effects of global warming is the rise in sea levels. As temperatures increase, glaciers and ice caps melt, adding freshwater to the oceans and causing their volume to expand. This, along with the thermal expansion of seawater, contributes to the gradual rise in sea levels globally. Rising sea levels pose significant threats to coastal communities, low-lying islands, and delta regions, leading to increased coastal erosion, inundation of land, saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources, and the displacement of populations.
Global warming also has socio-economic implications, impacting various sectors of human society. Changes in weather patterns and water availability affect agricultural productivity and food security, leading to crop failures, reduced yields, and increased food prices. The increased occurrence of extreme weather events and rising sea levels threaten infrastructure, including roads, buildings, and critical facilities like power plants and hospitals. Furthermore, global warming exacerbates social inequalities, as vulnerable populations, including the poor, marginalized communities, and developing countries, are disproportionately affected by its impacts.
In response to the pressing challenge of global warming, international efforts have been made to mitigate its causes and adapt to its effects. The primary approach to mitigating global warming is through the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This involves transitioning to renewable and low-carbon energy sources, improving energy efficiency, implementing sustainable agricultural practices, and adopting measures to reduce deforestation and promote reforestation. The Paris Agreement, signed by nearly every country in the world, aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius. The agreement sets forth commitments for countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions, enhance climate resilience, and provide financial and technological support to developing nations.
Adaptation strategies are also essential in addressing the impacts of global warming. These strategies involve adjusting human systems and natural ecosystems to cope with the changes brought about by rising temperatures. Examples of adaptation measures include building seawalls and flood barriers to protect coastal areas, implementing water management strategies to address water scarcity, developing heatwave preparedness plans, and promoting climate-resilient agriculture practices.
To further illustrate the complexities and significance of global warming, here is a list of ten important things to know about this pressing issue:
1. Global warming is primarily caused by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
2. The increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere leads to the greenhouse effect, trapping heat and causing a gradual rise in global temperatures.
3. Rising global temperatures have wide-ranging consequences, including the loss of biodiversity, shifts in ecosystems, more frequent and severe extreme weather events, and rising sea levels.
4. The impacts of global warming are felt worldwide, affecting both natural systems and human societies, but vulnerable populations and developing countries are often the most severely affected.
5. Mitigating global warming requires reducing greenhouse gas emissions through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable practices in various sectors, including energy, transportation, industry, and agriculture.
6. The Paris Agreement is a significant international effort to combat global warming. It aims to limit global temperature increase to well below 2 degrees Celsius and pursue efforts to limit the increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
7. Adaptation strategies are crucial in addressing the impacts of global warming and involve implementing measures to increase resilience to climate change, protect vulnerable communities, and manage resources effectively.
8. The loss of biodiversity due to global warming is a significant concern. Ecosystems, including coral reefs, forests, and polar regions, are under threat, leading to the potential extinction of numerous plant and animal species.
9. Global warming exacerbates water scarcity issues, as changing rainfall patterns and increased evaporation rates impact freshwater availability. This poses risks to agriculture, human health, and ecosystems reliant on water resources.
10. The impacts of global warming are interconnected, meaning that addressing this issue requires a holistic approach that considers the complex interactions between the environment, society, and the economy.
In conclusion, global warming is a critical issue that poses significant challenges to the environment, ecosystems, and human well-being. It is caused primarily by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to a gradual rise in global temperatures. The consequences of global warming are far-reaching, including the loss of biodiversity, extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and socio-economic impacts. Addressing global warming requires international cooperation, mitigation efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, adaptation strategies to cope with its effects, and a comprehensive approach that considers the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic systems.