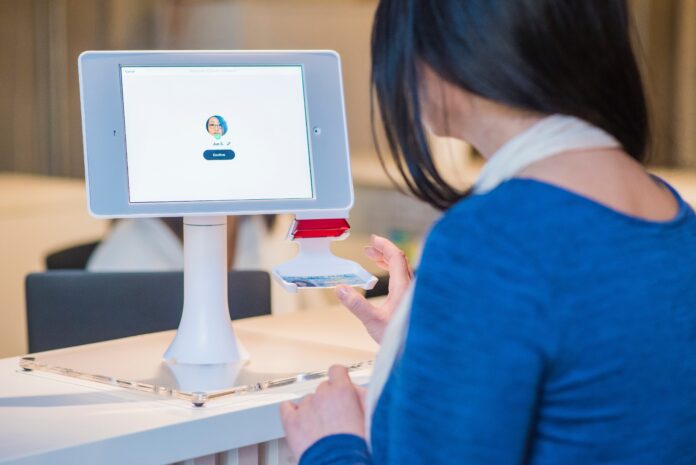
Facial recognition technology is an advanced biometric system that uses a combination of computer vision, machine learning, and pattern recognition algorithms to identify or verify individuals based on their facial features. It has gained significant prominence in recent years and has found numerous applications in various domains, including law enforcement, surveillance, access control, personal devices, and marketing. Facial recognition has sparked both excitement and concern due to its potential benefits and privacy implications. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of facial recognition technology and highlight five important aspects to consider.
Facial recognition technology, often referred to as FR, is a rapidly evolving field that has made significant strides in recent years. It involves the automated identification or verification of individuals by comparing their facial features to a database of known faces. The process typically begins by capturing an image or a video frame containing one or multiple faces. The system then analyzes the unique facial features such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the nose, and the contours of the face to create a facial template or a numerical representation of the face. This template is compared against a database of known faces to find a potential match. The matching process is performed using complex algorithms that are trained on large datasets and are capable of recognizing faces with high accuracy.
Now, let’s explore five important aspects of facial recognition technology:
1. Accuracy and Reliability:
The accuracy and reliability of facial recognition systems have improved significantly over time. State-of-the-art algorithms can now achieve near-human performance in identifying faces, making them highly efficient tools for authentication and identification purposes. However, it is crucial to note that the accuracy of facial recognition systems can be influenced by various factors, such as lighting conditions, pose variations, occlusions, and the quality of the input images. Additionally, biases can also arise in facial recognition systems, leading to higher error rates for certain demographic groups. Addressing these challenges is critical to ensure fairness and prevent potential misuse of the technology.
2. Privacy and Ethical Concerns:
Facial recognition technology raises important privacy and ethical concerns. The ability to capture and analyze individuals’ faces in real-time or from images and videos without their explicit consent raises questions about personal privacy. The widespread deployment of facial recognition in public spaces and the potential for constant surveillance can infringe upon civil liberties. Additionally, the storage and management of facial recognition data pose risks of unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential misuse. Robust privacy safeguards, regulations, and transparency measures are necessary to protect individuals’ rights and ensure responsible deployment of facial recognition technology.
3. Surveillance and Law Enforcement:
Facial recognition has become a powerful tool for surveillance and law enforcement agencies. It enables real-time monitoring and identification of individuals in crowded spaces, airports, border crossings, and public events. This can aid in enhancing public safety, identifying criminals, and preventing potential threats. However, the use of facial recognition in surveillance raises concerns regarding mass surveillance, indiscriminate data collection, and the potential for misuse. Striking the right balance between security and privacy is crucial to prevent overreach and protect civil liberties.
4. Biometric Authentication and Access Control:
Facial recognition is widely used for biometric authentication and access control systems. Many smartphones, tablets, and laptops now integrate facial recognition as a convenient and secure method for unlocking devices and authorizing transactions. By analyzing unique facial features, these systems provide an additional layer of security beyond traditional passwords or PINs. However, it is important to recognize that facial biometrics are not infallible, and there have been instances of unauthorized access through spoofing techniques using masks or manipulated images. Ongoing research and development are necessary to improve the robustness and anti-spoofing capabilities of facial recognition systems.
5. Social and Commercial Applications:
Facial recognition technology has also found applications in various social and commercial domains. It is used for sentiment analysis, emotion detection, age estimation, and gender classification in marketing and advertising. By analyzing individuals’ facial expressions, companies can gain insights into consumer preferences and tailor their products or services accordingly. Additionally, facial recognition is utilized in entertainment and gaming industries, enabling personalized experiences and virtual avatars that mimic users’ facial expressions. While these applications offer exciting possibilities, it is crucial to address concerns related to data privacy, consent, and potential manipulation of individuals’ emotions or preferences.
Facial recognition technology has emerged as a powerful and versatile tool with various applications in today’s world. It offers convenience, security, and efficiency but also raises significant privacy, ethical, and societal concerns. As the technology continues to evolve, it is imperative to strike the right balance between its potential benefits and the protection of individual rights and liberties. Robust regulations, transparency, and accountability measures are essential to ensure the responsible development and deployment of facial recognition systems
To address the concerns surrounding facial recognition technology, several organizations and governments have taken steps to establish guidelines and regulations. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union provides a framework for the protection of personal data, including facial images. It emphasizes the importance of obtaining explicit consent, ensuring transparency, and implementing appropriate security measures when using facial recognition technology. Similarly, some jurisdictions have imposed restrictions on the use of facial recognition by law enforcement agencies to prevent potential abuses and protect civil liberties.
Research and development efforts are also underway to improve the fairness and accuracy of facial recognition systems. This includes the development of more diverse and representative datasets to mitigate biases and the enhancement of algorithms to handle challenging conditions such as poor lighting or partial occlusions. Moreover, anti-spoofing techniques are being refined to detect and prevent unauthorized access through facial impersonation.
Public awareness and engagement are essential in shaping the future of facial recognition technology. Open discussions, consultations, and involvement of diverse stakeholders can help in establishing guidelines and policies that reflect societal values and ensure responsible use of the technology. Furthermore, transparency from technology providers regarding the capabilities and limitations of their facial recognition systems is crucial to foster trust and accountability.
The ongoing debate surrounding facial recognition technology extends beyond legal and regulatory aspects. It involves ethical considerations, including the potential for surveillance, discrimination, and unintended consequences. Striking a balance between security, privacy, and individual rights is a complex task that requires ongoing evaluation, dialogue, and collaboration between technology developers, policymakers, and civil society.
As the field of facial recognition continues to advance, it is crucial to recognize its potential impact on society and continuously assess and mitigate its risks. This involves not only technological advancements but also the establishment of robust legal and ethical frameworks that guide its development and deployment. By navigating these challenges effectively, facial recognition technology can contribute positively to various domains while respecting privacy, ensuring fairness, and upholding human rights.
In summary, facial recognition technology is a rapidly evolving field with significant implications for society. Its accuracy, privacy concerns, applications in surveillance and law enforcement, use in biometric authentication, and potential for social and commercial applications are five important aspects to consider. With responsible development, comprehensive regulations, and public engagement, facial recognition technology can be harnessed in a manner that maximizes its benefits while safeguarding individual rights and maintaining societal trust.